- Contrary to popular assumption, cryptocurrency wallets don’t actually keep coins like a wallet in your pocket.
- Rather, they operate as a central repository for the public and private keys needed to purchase cryptocurrencies and offer digital signatures that validate each transaction.
- Different kinds of crypto wallets exist, including tangible objects, software, and even paper.
- The best cryptocurrency wallet for you will largely depend on your unique trading requirements.
What are crypto wallets?
Users’ public and private keys are stored in cryptocurrency wallets, which also offer a user-friendly interface for managing cryptocurrency balances. They also support blockchain-based bitcoin transfers.
Some wallets even permit users to carry out certain operations with their cryptocurrency assets, such as purchasing and selling or utilizing decentralized applications. It’s crucial to keep in mind that transactions involving cryptocurrencies do not signify the “sending” of crypto tokens from your mobile device to another person’s mobile device.
In reality, when you transmit a token, your private key is used to sign the transaction and publish it to the blockchain network. The revised balance in both your address and the recipients will then be reflected in the network’s inclusion of your transaction.
Cryptocurrency wallets control the private keys that provide you the ability to conduct transactions as well as read the public ledger to show you the balances in your addresses.
How does it work?
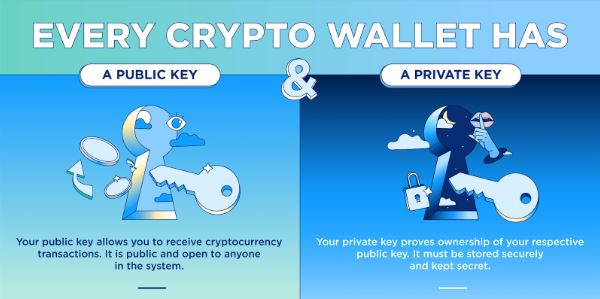
You must use a private key that has a series of unique codes to validate your address before you can carry out any of the required transactions. Your wallet type has a significant impact on both speed and security.
To transmit cryptocurrency, a user enters the public key of the recipient wallet and the desired amount, whether it be to pay for a future vacation or purchase a new watch. When a user wants to receive crypto instead, the procedure is reversed.
The private key must be used to “sign” a transaction every time cryptocurrency leaves a wallet. Depending on the type of wallet you use, that important step takes different forms.
Types of Crypto wallets

Hot wallet
Any cryptocurrency wallet that is online is referred to as a hot wallet. The majority of crypto wallet types are of the “hot” category since they are typically simple to use. Hot wallets are great for convenience because they are always on, but that same characteristic also makes them more susceptible to hackers. As a result, keeping sizable sums of cryptocurrency in a hot wallet is not advised.
Examples of Hot Wallets
- Web based Wallets
| Pros | Cons |
| Most crypto novices choose it since it is simple to use. | Entails putting your trust in a third party to protect your secret keys |
| Support many transaction types (buy, sell, swap etc.) | Maybe susceptible to hackers |
| Account security is contracted out to a reliable third party (exchange, etc.) | Web wallet computer is also vulnerable to dangers like viruses, malware, and keyloggers |
- Mobile wallets
| Pros | Cons |
| Simple mobile crypto payment sending and receiving | Only your phone is as secure as your holdings. |
| Extremely practical and simple to use | If device is lost or stolen, account may be hacked |
| One of the simplest methods to use cryptocurrency | Similar to a computer, a phone may be susceptible to malware and viruses. |
- Desktop Wallets
| Pros | Cons |
| Excellent for using a computer to securely carry out minor cryptographic operations | Maybe susceptible to malicious software or computer viruses |
| Useful and cost-free No one else has access to your private keys. | Your cryptocurrency could potentially be accessed by anyone who has access to your computer. |
| Some can be utilised for cold storage offline. |
Custodial Wallets v/s Non-Custodial Works
Custodial vs. non-custodial crypto wallets is a crucial distinction to discuss before moving on to different sorts of cold wallets. The main distinction between these alternatives is security rather than practicality and who is in charge of safeguarding a wallet’s private keys.
With a custodial wallet, a third party, such as a cryptocurrency exchange, holds a user’s private keys and makes use of them to “sign” transactions that have already been made on the owner’s behalf.
Users who don’t want to hassle too much with security and who aren’t very worried about entrusting a third party with their private keys should use custody wallets.
It’s generally not recommended to hold sizable quantities of cryptocurrencies in a custodial wallet due to dangers like hackers or even an exchange going bankrupt (which has happened before)
Non-custodial wallets are frequently chosen by more experienced crypto users or people who desire total control over their private keys. The owner of a non-custodial wallet is solely accountable for safeguarding their private key.
Non-custodial wallets don’t demand that a user put their faith in a third party to protect their accounts, but they do demand a high level of self-trust. Keep in mind that if a user’s private key is lost or compromised, their money could be lost forever.
Cold Wallet
As you might have imagined, offline or unconnected wallets fall under the category of cold wallets. Since the blockchain can only be accessed online, cold wallets are thought to be extremely secure and nearly immune to hackers. Since cold wallets normally demand a little more technical expertise, they are usually best suited for more seasoned users or people with substantial sums of assets
Paper Wallet
A paper wallet, as the name implies, is an offline wallet solution in which private keys are typed, printed, or both, and kept safe.

| Pros | Cons |
| Being entirely disconnected makes hacking impossible. | Paper is readily misplaced, taken, burned, or otherwise damaged. |
| Your private keys are not in the hands of anyone else. | More time and effort is needed to transfer cryptocurrency across wallets. |
| Including a QR code is optional and makes access easier | More technical knowledge is required. |
Hardware wallets
A hardware wallet provides safe private keys stored in a variety of formats for individuals who would rather use a more advanced solution.
These tangible objects, which frequently resemble USB thumb drives, remain inactive unless they are connected to a computer or mobile device.

| Pros | Cons |
| One of the safest ways to store cryptographic keys | Not free; costs $30 to $200 |
| When a transaction is uploaded to the blockchain, it is only signed using the private key online. | Can be difficult for those new to cryptocurrency |
| Accessible at most large electronic stores |
Which cryptocurrency wallet should I pick?
There is no ideal option for cryptocurrency wallets. Every style of wallet has unique benefits, functions, and trade-offs. So it’s truly up to you to consider what suits you and your unique demands the best.
The ease of a hot wallet would be ideal for folks with a high risk tolerance who wish to make frequent, rapid internet payments.
However, if you’re a little more cautious and want to keep your coins for a while, a safe offline device would be the best option.
Factors you need to consider:
- Hardware versus software
- Security components
- How intuitive it is
- Fees
- Backed coins
- Platform adequacy
- If you require DEX and DAPP integration
- Whether the wallet has fail-safe measures
- Reputation and longevity of the wallet in the market
Final Word
- Cryptocurrency wallets are a central repository for the public and private keys needed to purchase cryptocurrencies.
- They also offer digital signatures that validate each transaction. Some wallets even permit users to carry out certain operations with their cryptocurrency assets, such as purchasing and selling or utilizing decentralized applications.
- Your wallet type has a significant impact on both speed and security.
- Private keys are securely stored on a user’s computer hard drive by desktop wallets using encryption.
- Custodial vs. non-custodial crypto wallets is a crucial distinction to discuss before moving on to different sorts of cold wallets.
- The main distinction between these alternatives is security and who is in charge of safeguarding a wallet’s private keys.
- There is no ideal cryptocurrency wallet, so it’s truly up to you and your unique demands to choose the best solution for you.

